Recent security breaches, such as generative AI-based phishing attacks in 2023 and the 2018 hack of Facebook’s user data, have brought the relationship between artificial intelligence and cyber crime back into mainstream conversations. In particular in light of the recent rapid growth of the use of AI across industries and even in our personal lives, it has become more important than ever for the general public to trust in an organization’s ability to properly manage its AI systems and secure consumer data against advanced criminal activity.
If you are part of an organization looking to bring AI into your operational and cyber security systems, you’ll need to first understand what AI can do for your business. Not only that, but you’ll need to know the ways that cyber criminals are hacking into company AI systems for malicious purposes and even creating their own AI systems to disrupt organizations. AI-based cyber security solutions can also help you to counteract the threats posed by bad actors using AI.
Keep reading to learn the practical benefits of AI in the modern workplace, the potential cyber threats that malignant AI may pose to your organization’s data, and how your enterprise can safeguard itself against these new digital threats while still investing in practical AI solutions.
CURRENT IMPLEMENTATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN OPERATIONS
Though controversial in some circles, there is no doubt that artificial intelligence is rapidly becoming the next technological movement in modern business operations. AI has a vast and varied number of uses that can be implemented in every aspect of daily business operations.
1. Job Augmentation, Not Replacement
The increased use of AI in the workplace has sparked debates about whether digital technologies are here to replace human labor for good. This discussion has only accelerated as generative AI has become widely available, giving employers the ability to use AI to create images, text, and video that may seem authentic or human-created.
However, even as it has made incredible strides, AI still has many limitations that currently make it impossible to fully rely on it in place of human efforts. For example, AI lacks an understanding of human emotion or cultural context, and is unable to direct its actions with empathy, a very important aspect of human decision making.
Furthermore, when it comes to generative AI, although its output is very impressive, at its current stage of development there are noticeable errors. For example, generative AI’s text often contains erroneous information confidently presented as fact. This phenomenon, called AI hallucinations, is well known and means that humans need to carefully fact check AI-generated text. Additionally, images generated by AI sometimes have bizarre errors, such as its famous struggle with creating realistic hands and with printing text on its images. If a business needs to represent itself to the world with a new logo or a factually accurate article, relying on AI alone does not make sense.
Additionally, at its best, AI has the ability to make daily work tasks more manageable, rather than replacing humans altogether. Artificial intelligence and humans excel at different kinds of intelligence, and the best results come from keeping both in the workplace. AI can handle mundane and repetitive tasks without getting bored, tired, or unmotivated. AI can also conduct analysis tasks much faster than a human could, and, using generative AI, can create reports and even answer questions from humans in conversational language. However, humans need to work together with AI to decide how to act on the information received.
AI can make workplaces more efficient by making up for temporary labor shortages and completing time-consuming tasks through process automation. The automation of repetitive physical and mental tasks, such as physical inventory manipulation and data interpretation, can allow employees to focus on the tasks most critical to their given roles.
2. Business Intelligence

Business intelligence (BI) is key to any professional organization’s ability to accurately track and analyze its data, optimize workflow, and create short-term and long-term goals for its operations. In this way, AI and BI are complementary to one another. AI can be used to easily collect and organize large amounts of data. Analysts and managers can then use that data to make tangible decisions for operations, short-term or long-term projects, financial planning, and more.
3. Recruitment and Hiring Procedures
As many large companies are already aware, AI is becoming an increasingly common tool in pre-screening and selecting job candidates for open positions. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) can use AI to review the huge volume of applications much faster than a human could, selecting those that most closely match criteria that the employer is seeking.
Beyond candidate recruitment itself, certain AI hiring services are also offering automatic scheduling and redirection of strong candidates to other suitable positions in a company.
It is worth noting that employers need to be careful how they use AI for the recruiting process. In particular, AI can reflect and magnify any existing biases in your hiring process. As an employer, you need to understand how the algorithms behind your ATS work to avoid discrimination in hiring, and missing out on talent.
4. Cyber Security Measures
While this article serves as a caution about the cyber crime threats of AI, AI can also have beneficial effects for cyber security. One of AI’s most complex uses is managing cyber security threats. AI can be taught to spot malware and viruses, for instance. Over time, it can become faster than humans at spotting cyber threats to your systems through automated threat detection. On average, AI implementations have been found to reduce the average cost of an organization’s data breach scenario by $230,000.
One of the ways that AI can enhance cyber security is through its machine learning capabilities. Essentially, through pattern recognition and prediction, AI can learn about the behavior of cyber criminals and better anticipate, prevent, or respond to, cyber attacks.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND CYBER CRIME: KNOWING THE THREATS

AI is a multifaceted tool that can be used for both data collection and organization, as well as the protection of this data against outside forces. Because of the widespread adoption of AI in business operations in recent years, artificial intelligence and cyber crime protection have developed an interdependent relationship in contemporary cyber security models.
AI can greatly heighten the efficiency of any data security system by spotting potential threats before they even come to fruition and quickly squashing incoming cyber attacks at beyond-human speeds. However, by remaining focused on the benefits of AI integration into various operational systems, many business owners are unaware of the threats that outside AI systems may also pose to their businesses, as well as the vulnerabilities of their own AI systems.
Highly publicized cyber attacks in our home state of Louisiana and across the world have revamped concerns about the further integration of AI technologies into daily life, especially in business operations. Furthermore, now that automated phishing, malware, and ransomware processes can be completed by artificial intelligence, AI-assisted attacks are becoming more mainstream. The advancement of AI systems is leading to an evolution of the complexity of even lower-level cyber attacks.
TOP 4 THREATS THAT AI COULD PRESENT TO YOUR ORGANIZATION
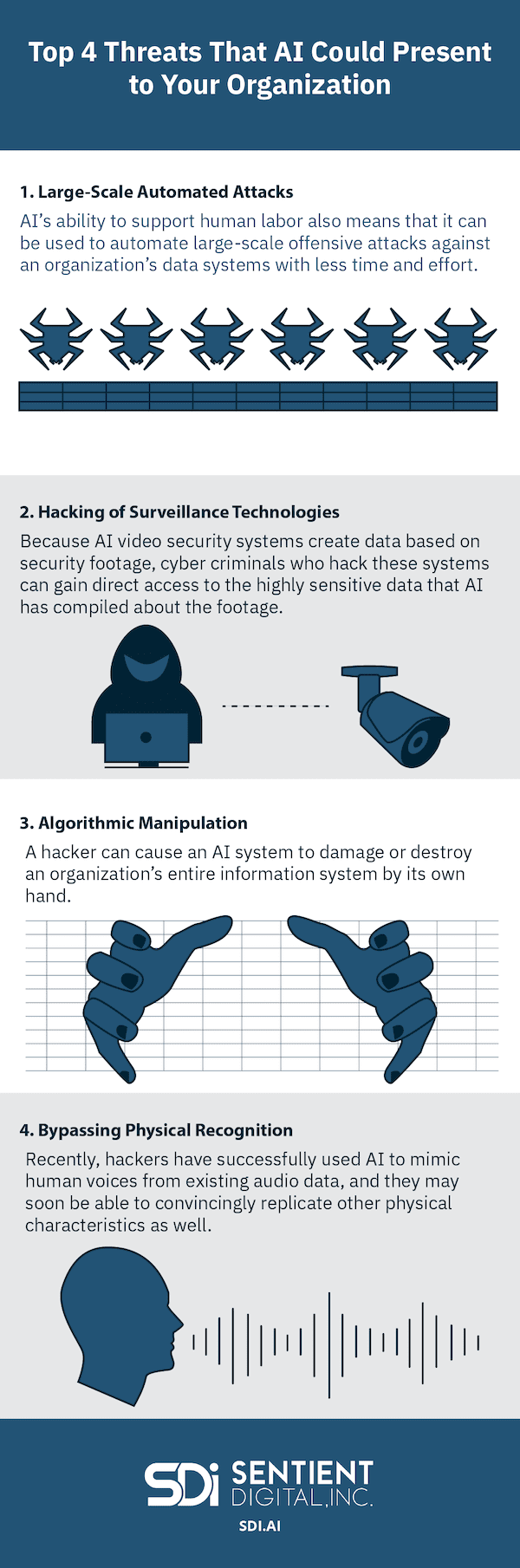
Learn more about the top 4 threats that AI could present to your organization below! Please feel free to share our infographic on social media, or copy and paste the code below to embed it on your website:
<img src="https://bit.ly/top4AIthreats">
<p>Top 4 Threats That AI Could Present to Your Organization - An infographic by the team at <a href="https://sdi.ai/">Sentient Digital, Inc.</a></p>1. Large-Scale Automated Attacks
AI’s ability to mimic human thought patterns and modes of operation at rapid speeds means that these systems can be trained to carry out coordinated cyber attacks without a human cyber criminal actively dictating the AI’s behavior. With AI, cyber criminals can devote less time and effort in coordinating a large attack on an organization’s data system, instead teaching an AI system to carry out a cyber attack with little to no human involvement.
With AI-powered systems able to launch attacks rapidly and on a large scale, trying millions of password combinations every second, the threat of unauthorized access is significant. Not only that, but these systems can constantly improve their efforts with adaptive learning algorithms. Organizations have little time to remedy vulnerabilities with AI identifying and targeting them in a matter of seconds.
To defend against artificial intelligence in cyber crime, organizations must likewise leverage AI for their own protection. AI-powered cyber security technologies can assist with finding such threats and reacting to them with the same speed. Moving forward, organizations will need to constantly stay one step ahead of cyber criminals by keeping up to date with the latest AI developments in the cyber security field. As always, organizations would also be wise to invest in proactive cyber security monitoring.
2. Hacking of Surveillance Technologies
AI-based video footage security systems intake security footage and process data from it. Object and facial recognition technologies allow these systems to compile visual data from footage and create reports based on that data. If a hacker were to gain access to AI-based surveillance footage, they would not only have physical security footage, but also access to the data that the AI has ascertained about the footage.
3. Algorithmic Manipulation
Hackers can break into AI data systems and manipulate an AI algorithm’s prioritization of information. By adjusting the algorithm to change what an AI system sees as valuable or not valuable data, a hacker can cause an AI system to damage or destroy your organization’s entire information system by its own hand. Because these attacks directly impact the AI system’s machine learning process, which is the basis of how AI systems learn to process the information they encounter or are presented with, these types of attacks on AI systems are extremely difficult to resolve.
4. Bypassing Physical Recognition

As AI systems become increasingly capable of replicating human behavior, they may be able to convincingly replicate the physical characteristics of specific individuals. In a hallmark 2019 cyber attack, a hacker utilized AI to mimic the voice of a European company executive to transfer over $240,000 from the company’s funds directly into the hacker’s account. The employee who answered the AI’s call was certain that the AI’s voice was that of the company executive.
In many instances, the exact ways that AI can make operations efficient and keep data secure are its largest vulnerabilities. Despite its utility and increased usage in modern operations, many organizations lack guidance on how to safely implement AI technologies in their systems. In the public domain, there is also a lack of information on how organizations can adequately defend themselves against cyber threats.
THE FUTURE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND CYBER CRIME
Though the current and future advancements in the realm of cyber security are clearer, the future of artificial intelligence and cyber crime is difficult to predict. What could the advancement of AI do for the future of cyber security and, conversely, for cyber crime? What cyber crimes should any business utilizing AI technologies be wary of?
According to recently published research by members of the Oxford Internet Institute at Oxford University, AI’s ability to work on such a large scale and its ability to create a convincingly human appearance will make artificial intelligence crimes more difficult to detect in the future. Cyber criminals will likely produce more mature, malignant AI systems with the ability to create more convincing images of human behavior. Even lower-level cyber attacks will be difficult to spot immediately, because they will have been crafted with AI technologies that have learned to replicate human behaviors and language more accurately.
One concerning possibility for the future of artificial intelligence and cyber crime is phishing emails that use more convincing and less stilted language, especially if more employees continue working remotely. Other potential issues include malicious files or data made to appear entirely benign, as well as deepfakes (AI-based videos and photos that recreate the likeness of individuals in fake scenarios). At the very least, the already complex nature of AI and AI-related cyber crimes will only become more difficult to track and address in the future.
USING ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE TO PROTECT YOUR BUSINESS AGAINST CYBER CRIMES

As is the case with any technology that handles sensitive data, there are dangers to implementing AI without understanding how to best maintain its security and utility. Thankfully, as more businesses start integrating AI technology, there are stronger and more widely available cyber security measures your team can utilize to protect sensitive data and AI systems against a cyber attack.
Since AI itself also provides a growing and reliable source of cyber security tactics, knowing how this tech can be implemented in your cyber security will be key to your organization’s protection.
1. Advancing Cyber Resilience Strategies
Cyber resilience describes a data system’s ability to continue its operations during or after a cyber attack. It also considers the system’s ability to restore stolen data or mechanical operations after data or system damage has occurred.
Cyber resilience is a vital aspect of cyber security, since it is directly involved in the maintenance of recovery solutions in the instance of a system attack. AI-driven data backups and system recovery protocols are integral to developing your organization’s cyber resilience.
AI can provide IT departments with potential actions to take in the recovery of data, reorganizing data until the main system is fully recovered, and even optimizing the backup process to make it more efficient. The Department of Homeland Security even offers assessment packages that can help an organization evaluate the current status of its cyber resilience.
2. Implementing Offensive and Defensive Security Solutions
Artificial intelligence is an essential part of modern cyber security, especially when it comes to quickly identifying threats. The best way to protect your business is to use both proactive and reactive cyber security, taking advantage of AI to help protect your business from threats. For instance, AI technologies are now being used to improve the ability of cyber security systems to engage in threat hunting and monitoring. Both are major proactive security measures that can prevent cyber attacks before they ever occur.
When it comes to using AI to detect threats, two of the most important approaches today are Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) models. With NLP and ML, AI can review significant amounts of data quickly, recognizing patterns and proactively predicting or reactively identifying cyber threats.
Natural language processing, which allows AI to process and understand human language, can be trained to identify phishing attacks in emails, for instance. By training NLP models on a significant amount of data, including phishing emails as well as benign emails, it can learn how to effectively review sender information, subject lines, body text, outbound links, and attachments for malicious intent. These models understand the type of language that is associated with phishing, including misspelled words, contradicting information, and a sense of urgency.
Machine learning, on the other hand, uses algorithms to process data, both learning from it and making decisions based on it. These models are increasingly being used to detect anomalies for cyber security purposes. They can recognize patterns that are outside of the norm which may present a security risk. By presenting these models with data on benign network activity, such as user behavior, traffic patterns, and system performance, it can learn what is normal and what is an anomaly. Unusual login attempts, unexpected increases in traffic, and abnormal systems changes, for instance, could represent a cyber threat.
3. Hiring Artificial Intelligence and Cyber Crime Experts
Beyond hiring standard IT personnel, any organization looking to integrate AI into its systems should also consider hiring either internal or external AI security and maintenance experts. These highly skilled professionals can implement regular security protocols into these systems, as well as ensure the effectiveness of an AI system’s algorithms.
LIMITATIONS AND CHALLENGES OF RELYING ON AI FOR CYBER SECURITY
In today’s AI-enhanced landscape, there is no doubt that AI offers great potential for improving cyber security. In fact, organizations that do not leverage AI for their cyber security are at risk of falling behind and falling victim to vulnerabilities from AI-powered cyber crime. But there are limitations and challenges with relying on AI for cyber security that must be kept in mind. Organizations should take care not to put all of their trust into automated systems—human oversight is still a critical component of cyber security.
Over-Reliance on Automated Systems
Becoming too reliant on automated systems carries significant risk for organizations. By assuming that AI is fully capable and completely accurate, effectively managing your cyber security from end to end, you could become complacent and miss AI’s blindspots. As a result, there could be vulnerabilities in your systems that AI isn’t able to identify and subsequently address. AI’s training may fall short when it comes to new cyber crime strategies or more sophisticated cyber attacks, for instance.
As a result, organizations should invest in a two-pronged approach that involves both artificial intelligence and human cyber security professionals. Human workers can support their own efforts with AI tools, as well as regularly update the AI’s training so it can continually improve and take emerging information into account.
AI Technologies Can Be Bypassed or Exploited
AI technologies, and especially those that involve machine learning, often learn from data. That presents a risk, as cyber criminals could attempt to use this data or an AI’s algorithms against it. For instance, cyber attackers who study AI-powered antivirus technologies may be able to tweak their malware in such a way that it is no longer recognizable to the AI, allowing it to bypass the system.
As much as possible, such risks should be accounted for from the beginning with AI that is used for cyber security. This can take the form of adversarial training as part of an AI’s training phase. By feeding manipulated data to the AI during its training, it can better learn how to identify and respond to such attacks. Another important component is human intervention. An organization’s cyber security experts should be responsible for monitoring AI cyber security systems on a regular basis, as well as updating it over time to learn about the latest tactics in cyber crime.
Human Oversight Remains Critical
No matter how advanced AI becomes, it will always require human oversight. Cyber threats are complex, and human experts are better equipped to see and understand certain nuances of cyber crime within a larger context. Statistical anomalies do occur, which could cause AI to mistakenly identify a benign activity as a threat. A human cyber security expert could quickly look at the context surrounding this activity and recognize that it does not pose a threat.
Whenever an organization chooses to implement AI technologies into its cyber security, it is crucial to teach your cyber security personnel about these technologies. A cyber security team should be able to effectively leverage these technologies while also accounting for their limitations from the very beginning. Processes should be put into place immediately for cyber security professionals to monitor these technologies on an ongoing basis, audit them to assess their effectiveness on a periodic basis, and intervene to provide assessment and action on complex or borderline cases.
Effectively Identifying and Prioritizing Cyber Security Objectives
Without properly identifying and prioritizing your organization’s cyber security objectives, it will be difficult to use AI to its full advantage. This involves:
- Understanding Your Biggest Threats: Knowing the specific threats that present the most danger to your organization, now and in the future, can help you find the right AI solutions to mitigate those critical threats.
- Prioritizing Proactive versus Reactive Cyber Security: While the best approach to cyber security involves a combination of both proactive and reactive measures, it’s important to know which takes priority at your organization. The threats facing your organization, as well as your risk tolerance, will be unique to you and impact how you divide your attention and resources between proactive and reactive cyber security. AI can be an effective tool for both, supporting threat hunting, anomaly detection, and other proactive tactics, as well as incident response and other reactive activities.
- Adhering to Your Ethics: AI technologies come with important ethical considerations. In order to use AI ethically from the outset, an organization needs to understand the ethical questions that arise with AI usage, such as biases and privacy concerns. Before AI technologies are implemented, there should be processes in place to ensure they are deployed ethically and with proper human oversight.
By addressing these limitations and challenges, organizations can successfully leverage AI for cyber security purposes, ensuring a robust defense against the threats of today and the days to come.
CONTACT US FOR AI AND CYBER SECURITY SUPPORT
Ensuring that your organization prioritizes cyber security means hiring experts in the AI and cyber security realm. If you’re part of a company or government organization looking to expand its defenses against cyber crime, SDi is here to help.
Whether you’re looking for support or solutions for a specific project or in the long term, our experts are ready to meet your unique needs. Call us today at 504-308-1464 or contact us online to learn how we can secure your organization against cyber threats.




