Information assurance is the cornerstone of any successful cybersecurity framework, and to make sure that your protocol is both effective and ironclad, you must know the five principles of information assurance. In an era in which businesses collect more data than ever before, it is essential to learn how to adequately protect your business’ information via the most state-of-the-art information assurance methods available to you. The first step is understanding what constitutes information assurance.
What is Information Assurance and Why Does It Matter?
Implementing these principles will require some investment of time and resources up front, but it can definitely save your business a lot of money down the road. According to IBM, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was over four million dollars, with the cost of data breaches going up over the preceding three years. No matter the size of your business, you cannot afford not to take information assurance seriously.
To start, what is information assurance? In short, information assurance is the protection of information and how it is processed, used, transferred, and stored. There are 5 principles of information assurance:
- Availability
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Authentication
- Nonrepudiation
In our increasingly digitized world, the principles of information assurance have become extremely important. Whether you work for a bank, a talent agency, or a cybersecurity firm, most organizations these days deal with sensitive information of some kind. This includes everything from your company’s bank account number, to your customers’ email addresses and credit card numbers, to any Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) you come across while completing contract work for the U.S. government. From our cybersecurity services, to the systems engineering and software development services we perform with RDA, Inc. a high tech contractor we acquired in 2021, information assurance has long been critical to our work. However, everyone can benefit from strong information assurance protocols, no matter the industry.
If this sensitive data falls into the hands of a hacker, the consequences can be devastating. On average, organizations that are hacked lose $1.1 million to damages and repairs. The data breach can also harm your public reputation, and you may even become embroiled in a data privacy lawsuit. To avoid compromising your sensitive data and risking financial ruin, you must follow the principles of information assurance.
Information assurance is a crucial part of making sure your business protects its finances, runs its operations smoothly, and preserves the trust of your customers and partners. Information assurance involves putting comprehensive security measures into effect to safeguard the data and systems for which your organization is responsible. Effective information assurance can include best practices for utilizing encryption, access controls, network security protocols, and employee training on security policies. Continuous monitoring, auditing, and updating is also key to identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can cause a situation that will cost your organization significant time and money. Implementing robust information assurance policies demonstrates to your customers and partners that you understand the critical importance of protecting their information. Learn about the 5 principles of information assurance and incorporate them into your business model today.
WHAT TO PROTECT WITH INFORMATION ASSURANCE

As mentioned earlier, information assurance describes the set of processes used by an organization to keep its data and information systems safe from criminals. But what exactly does that encompass?
Typically, a company’s information assurance infrastructure includes secure methods for creating, transporting, and storing sensitive information. These security measures should be designed to detect and react to threats. Proactive monitoring and mitigation can help address threats before they ever reach your business, keeping your private information and sensitive data safe from cyberattacks.
When we talk about information assurance, we usually think about digital assets, since most organizations store their valuable information in a computing network. However, information assurance actually encompasses both digital and physical information channels. So, when you’re determining your desired result, you need to emphasize which information channels and pillars you want to see integrated, balancing services and privacy. Not every information assurance plan is created equal, so be specific about your needs and goals in order to achieve them.
Even if you do not store your sensitive information in file cabinets, the physical components of your business’ information processing need to be considered when establishing security measures. For example, where are your data centers located? How many remote endpoint devices are accessing your network? Assess your information repositories, both digital and physical, ahead of time to ensure that all databases and all sensitive information is accounted for. When you know what data you need to protect and where, you can better understand and implement the principles of information assurance.
GETTING STARTED WITH INFORMATION ASSURANCE
The first step to implementing a robust information assurance system is to determine the current status of your organization in this respect by reviewing your information network. All of the locations in which your business data is generated, processed, saved, or transmitted should be documented. Understanding your existing infrastructure can help you prepare to better implement the principles of information assurance, ensuring that you have the right scanning tools available. Then, by creating a system for prioritization that involves your whole organization and educating your team on the best cybersecurity practices, you can secure your organization from the ground up. To learn more, check out this map of how sensitive information flows through your business.
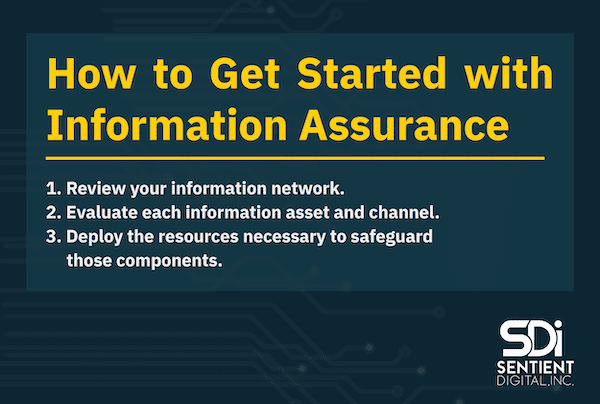
Each information asset and channel should then be evaluated in terms of its value to your organization. In addition, you should consider how much damage could potentially result if an asset or channel’s information fell into the wrong hands.
Once you identify which parts of your information system need the most protection, you can deploy the resources necessary to safeguard each of those components. Remember that even small businesses are at risk, too. In fact, small businesses account for 43% of data breaches. While small businesses may not have equal resources to devote to information assurance, compared to medium and large organizations, it is important for them to take this issue seriously, to avoid costlier issues down the line.
Cyberattacks happen to organizations of all sizes, not just large companies or government agencies. When cyber attacks occur, these small businesses are hit hard, losing large percentages of their profits on fixing their damaged networks and making up for lost productivity. So no matter the size of your business, ensure that you have a cybersecurity plan in place that aligns with the principles of information assurance.
WHY PRIORITIZE SOME ASSETS AND CHANNELS?

You may be wondering why you can’t simply safeguard every information asset and channel equally well, making it difficult to hack any of it. Most organizations have an enormous amount of assets and channels, but a finite amount of resources. Securing your information requires financial resources, personnel, and computing power.
Not only that, but the more secure a system is, the more challenging it can become for that system to actually remain functional. For example, a sealed car without any doors or windows would be incredibly secure, but not at all practical for you to use.
The same principle is true for the sensitive data your organization processes and stores. While you want to keep your data away from potential hackers, you still need to be able to access that information. You may need to be able to transmit it to employees or third-party contractors as well. It should be carefully safeguarded, but also remain accessible to those who need it with reasonable ease and speed.
For each component of your information system, you should evaluate its benefits to your business alongside its security risks. One way to think about an asset’s risk factor is in terms of the likelihood multiplied by the impact. What are the odds of this information component being breached? And what would the consequences be for your business operations, staff, and customers if it were compromised?
Knowing the answers to these questions and following the 5 principles of information assurance can help you create a successful system of risk management and prioritization.
THE 5 PRINCIPLES OF INFORMATION ASSURANCE

Learn more about the principles of information assurance below! Please feel free to share our infographic on social media, or copy and paste the code below to embed it on your website:
<img src="http://bit.ly/infoassuranceprinciples">
<p>The 5 Principles of Information Assurance - An infographic by the team at <a href="https://sdi.ai/">Sentient Digital, Inc.</a></p>These 5 principles of information assurance will help guide you as you evaluate each component or asset that handles sensitive information in your organization. It’s important to note that these principles do not act independently of each other. They are interrelated, connecting and enabling each other in the production of a strong information assurance framework. Let’s break down the principles essential to a secure information system and go through some information assurance examples for you to consider.
1. AVAILABILITY
Availability refers to how users are given access to sensitive information within your enterprise’s infrastructure.
Privileged information should not be readily available, as that can make it all too easy for hackers to obtain. But if the data is too difficult to access, then employees might not be able to perform critical job functions in a timely manner, costing your company lost time and revenue. Balancing these two considerations is critical to the information assurance principle of availability.
Availability also takes into consideration if and how sensitive information will be accessed, even if the information systems fail partially or fully. For instance, if a database failover occurs, ideally employees would still be able to access the information most critical to their business operations.
To ensure the continued availability of sensitive information only to a select few, security professionals will generally put measures such as firewalls and load balancers into place. An increase in storage capacity and channel reliability also helps to preserve the availability, ensuring that the principles of information assurance don’t compromise accessibility.
2. INTEGRITY
Integrity, as a principle of information assurance, means that your sensitive data is not tampered with in any way.
Antivirus software, penetration tests, and other security measures are often employed to ensure that your data’s integrity is not compromised by hackers. If malicious code or malware did manage to infect the data, your sensitive information could potentially be altered or deleted. Ideally, your company would use proactive cybersecurity measures to keep intruders from ever accessing your data in the first place.
Integrity also relates to user controls designed to prevent any meddling with sensitive data, making user authentication a cornerstone of the identity principle. Privileged users need to understand how to properly send information from one location to another without accidentally altering the data—or situating the data in such a way that it is easier for hackers to access. Failing to accurately authenticate a user leaves your sensitive information and data open to unauthorized alteration, meaning that a hacker or other hostile party could change your content. Consequently, comprehensive authentication measures are a must in the principles of information assurance.
Some organizations use hash signatures when transmitting sensitive data from one location to another. Hash signatures can serve the objective of data integrity by providing a way to detect any changes to data. When a hash value is created from the original data and encrypted, this signature can later be compared against a hash created from the same data. If the hashes do not match, it indicates the data has been altered or corrupted. The use of hash signatures allows them to confirm that the data has not been compromised while in transit.
3. CONFIDENTIALITY

Perhaps the most important among the information security principles is confidentiality. Only users who need to access sensitive information should ever be able to view, store, alter (in approved ways), or transmit this data.
Confidentiality must be maintained in terms of data as well as access or permissions. Thus, confidentiality is preserved not only through access controls, but also data encryption methods. When data encryption is utilized, users without access to the information will just see nonsensical text. Only users with an encryption key, or a password of some kind, will be able to view the information as written. Information confidentiality not only helps companies safeguard their ideas and data, but also protects customers from having their personal information stolen. Simple mistakes, such as housing sensitive information on an unsecured server, can cost you a lot of money in the long run, putting a large amount of personal data at risk.
4. AUTHENTICATION
Authentication means that there need to be controls in place to ensure that users are who they claim to be. Users must provide evidence of their identity before accessing any confidential information.
Authentication methods can be relatively common and easy to utilize, such as passwords, scannable cards, or multifactor authentication. In particular, multifactor authentication is important for information assurance because it is relatively straightforward to use, but requires more than merely entering a password. Passwords and scannable cards can both be stolen, but a user is unlikely to both have their login credentials taken and their phone stolen at the same time. Multifactor authentication involves having a user clear two or more identification barriers to gain access, such as entering their password plus a code sent to their phone via text message. This makes it much harder for unauthorized users to access a system. Even if a password is compromised, an attacker would likely also need physical access to the user’s phone or other device. Overall, multifactor authentication helps to reduce the risk of illegitimate access to sensitive information, account takeovers, and ransomware attacks by ensuring only the legitimate user can access sensitive information or systems, while also only minimally inconveniencing legitimate users. Implementing multifactor authentication is a strongly suggested step for many organizations to take to strengthen information security.
Authentication methods can also be more complex, such as biometrics tools capable of scanning your eyes or fingerprints. However, it is worth noting that there are additional privacy concerns when you are gathering biometric data about your employees to use an authentication method, so it is important to comply with applicable legal requirements and best practices.
Regardless of the information assurance methods you choose for authentication, it is a critical principle. When authentication is compromised, it damages organizations’ reputation as well as their infrastructure, proving just how vital strong authentication mechanisms are.
5. NONREPUDIATION
Nonrepudiation is a word often used in legal contexts, but it can be applied to information assurance procedures, too. Nonrepudiation means that when information is transferred, there needs to be proof that the action was successfully completed on both the sender’s end and the receiver’s end.
Nonrepudiation ensures accountability on both sides of an information transaction. This is critical for information assurance because it provides evidence of actions, such as sending a message or accessing data. With cryptographic proof of actions, nonrepudiation is particularly helpful in that it makes it difficult for insiders to cover their tracks if they compromise security. While no one wants to think that someone within an organization could intentionally access data they should not, guarding against this scenario is a necessary element of information assurance. Overall, nonrepudiation is vital for auditing, forensics, and holding parties responsible for complying with policies. This principle helps to ensure that users are who they say they are and that the data has not been altered during its transmission. Nonrepudiation is commonly tracked through file logs and verified cross-network data exchange systems.
HOW PRINCIPLES OF INFORMATION ASSURANCE HELP IN PRACTICE
Every modern organization needs to understand how to plan and execute a successful information assurance system based on solid information security principles. The cybersecurity landscape is constantly changing, but while the best practices for information assurance methods will also need to evolve, the overarching principles remain consistent. All businesses deal with sensitive information that could be disastrous if tampered with or destroyed, whether intentionally or accidentally. Altered or stolen sensitive information can lead to social security or credit card numbers falling into criminals’ hands, huge losses in both personal and global revenue, and many other damaging consequences.
So how do the principles of information assurance help avoid those disasters? Let’s take a look at the recent Louisiana OMV MOVEit data breach, the 23andMe data breach, the hack of multiple high-profile Twitter accounts, and Equifax data breach as examples.
Security Lessons from the Louisiana DMV MOVEit Data Breach
In the spring of 2023, the Louisiana Office of Motor Vehicles experienced a massive data breach, believed to impact everyone with a Louisiana driver’s license, ID issued by Louisiana, or car registration. This attack was serious in terms of the number of people affected, potentially 6 million, and how much information was obtained about each person. The state of Louisiana noted that, while not all information was obtained for everyone, for each person it “included name and one or more of the following: address, date of birth, Social Security number, driver’s license, learner’s permit, or identification card number, height, eye color, vehicle registration information, and handicap placard information.”
MOVEit is a third party file transfer software whose “Zero-Day Vulnerability” allowed in the attack by a group of Russian hackers. Which of the principles of information assurance were violated in this attack? According to the law firm representing the plaintiffs in class-action lawsuits against Progress Software, the owners of MOVEit (regarding the wider MOVEit data breach, which affected many organizations besides Louisiana OMV, which may not be included in the lawsuits), the Progress Software did not correct the vulnerability in the software, even though it had existed since 2021. If true, this could mean a violation of the integrity principle, because the software did not adequately protect the data from hackers.The lesson to takefrom this could be the importance of carefully vetting third-party vendors to ensure they comply with information assurance principles.
How Companies Choose to Respond To Data Breaches and What It Says About Their Information Assurance Practices: 23andMe
How an organization responds to a data breach can also provide some insight into how it implements the principles of information assurance. In October 2023, it was revealed that millions of users of the genetic testing company 23andMe had their data stolen and offered for sale on the dark web. The hackers apparently obtained the logins of fewer than 15,000 users but were able to benefit from an optional, automatic data-sharing feature of the platform to access the data of over six million users.
After an investigation, 23andMe wrote to victims of the attack that the problem was their failure to use unique, up-to-date passwords, rather than the fault of 23andMe. Following the breach, 23andMe reset the password of every user and made multifactor authentication (MFA) mandatory.
However, while it is true that user behavior can impact information assurance, an organization must take into account human nature. In particular, information assurance policies and procedures should counteract the risks posed by common user behaviors such as repeating passwords across accounts, refusing to change passwords periodically when it is not required, and the desire not to adopt MFA when it is optional. It appears that 23andMe did not implement an important authentication best practice for information assurance, by not requiring MFA prior to the attack. Regardless of how the lawsuits against 23andMe turn out, the company’s apparent position that certain well-known user behaviors were to blame for the breach shows the importance of considering how information users and stakeholders are likely to respond to your information assurance policies.
SECURITY LESSONS FROM HACKED TWITTER ACCOUNTS
According to the New York Department of Finance’s report on the July 2020 Twitter attack, the first tactic used was social engineering. This involved the hackers calling Twitter employees, posing as Twitter IT support, and gaining their credentials via a phishing website. With this access, the hackers explored Twitter’s internal network, and through further calls, eventually they obtained employee credentials that allowed them to take over other users’ accounts. The hackers then gained access to early Twitter users’ accounts, which are valuable enough that they can actually be sold. In the next phase of the attack, the hackers took over verified Twitter accounts to ask for cryptocurrency. They began with cryptocurrency-focused account, but then switched to the accounts of celebrities, politicians, and companies.
All 5 principles of information assurance were violated during this attack:
- Nonrepudiation was compromised because the hacker was able to appear as if they were Joe Biden, Elon Musk, and other public figures.
- Users who sent Bitcoins to the hacker did so because the integrity of this sensitive information had been meddled with, and they believed the money would be directed to someone else.
- Although there were numerous authentication measures in place, the hacker was able to steal proof of identity through phishing and bypass other controls that allowed them to reach the admin panel.
- The sensitive information in this case was too available to outside users, and thus the confidentiality usually assumed for private social media accounts was violated.
Twitter has since recovered from the attack and is working to strengthen its information assurance practices. But all organizations can learn from this and similar cyberattacks when forming their information assurance plans; even unsuccessful information assurance examples can teach us valuable lessons.
Diligently considering and practicing the 5 principles of information assurance will help your organization avoid disrupted business operations, lost time and revenue, and damaged customer relationships.
SECURITY LESSONS FROM THE EQUIFAX BREACH
In March 2017, millions of people’s personal identification data was stolen during a hack against Equifax, a multinational consumer credit reporting agency. The attack highlighted major failures in following the principles of information assurance. Several security vulnerabilities allowed the cybercriminals to enter the company’s seemingly secure data systems and exfiltrate terabytes of data.
The hackers initially entered a consumer complaint portal. Because of the Equifax systems’ inefficient segmentation, they were able to move to different outlets and servers. Apache Struts, the software provider for Equifax, discovered the CVE-2017-5638 vulnerability within the same month of the attack.
That same month, Apache Struts quickly released a patch for the exposure. However, none of the multiple vulnerable systems were flagged or patched during Equifax’s IT department scans.
From May through July, the attackers were able to find usernames and passwords of Equifax users stored in plain text. This gave them further access to the legal names, social security numbers, birthdays, addresses, and, in some cases, driver’s license numbers of these users.
By the time the hack ended, the attackers obtained 143 million individuals’ personal information, about 209,000 credit card numbers, and documents with further personally identifiable information for about 182,000 people. The breach included victims in the U.S. as well as in the U.K. and Canada. The company also did not announce the attack until September, leading to further customer distrust.

Equifax violated all 5 principles of information assurance during this attack:
- Nonrepudiation was compromised because the hackers could appear in a consumer complaint channel without registering as a security threat.
- There were not enough authentication measures in place to prevent the hackers from gaining access to additional information using only usernames and passwords.
- Equifax failed to protect users’ information in several countries, making it too available to outside users.
- Equifax’s user data being too widely and plainly available also demonstrated a breach in confidentiality. User data was not handled privately or securely within Equifax’s data systems. In addition, the users had no clue that their data was at risk while utilizing Equifax’s services.
- The hackers were able to go undetected because Equifax neglected the integrity of its digital systems. These cybercriminals could encrypt the stolen data and move it to other portals because Equifax failed to inspect encrypted traffic. While Equifax had the tools to decrypt, analyze, and re-encrypt internal network traffic, the company did not renew its public-key certificate, allowing the attackers to go unnoticed for 76 days.
Since the attack, Equifax has restaffed its C-level executives and spent $1.4 billion on cleaning costs. These costs include incremental costs to transform the company’s technology infrastructure and improve its application, network, and data security. Equifax also reached a record-breaking settlement with the Federal Trade Commission in July 2019 to conclude a class-action lawsuit, paying at least $1.38 billion to resolve consumer claims.
If Equifax had put the principles of information assurance into practice, this breach would not have occurred and the company would have avoided a major loss in business rating, consumer trust, time, and revenue.
ESTABLISH STRONG INFORMATION ASSURANCE PRACTICES WITH SENTIENT DIGITAL

Implementing the principles of information assurance into your business is crucial. Whether you’re handling sensitive government information or customer payment information, it’s important to ensure that this data does not become accidentally altered or fall into the wrong hands. These cyberattacks can damage not only your infrastructure but also your reputation and client relationships, making these principles essential to a secure information system. Regardless of the size of your business, its important to invest resources into improving your information assurance.
Choosing an experienced technology solutions firm to advise and augment your in-house IT staff can enhance your business’s cybersecurity preparedness. External specialists bring up-to-date knowledge of rapidly evolving threats and best-practices for organizational cybersecurity policy. With the resources to comprehensively audit vulnerabilities, implement multi-level controls and cutting-edge monitoring tools, technology consultants can assist you in establishing robust incident response protocols. Dedicated cybersecurity partners equipped with state-of-the-art understanding and resources will boost your effectiveness in tackling digital threats. The right partner will work together with your team, leveraging your organizational knowledge to ensure sophisticated cyber readiness that rises to match the risks inherent in modern business operations.
At Sentient Digital, we have years of experience helping businesses not only develop information assurance plans, but use practical and affordable technology to integrate those plans into their daily operations. We provide customized solutions that further your business objectives while keeping your systems and data safe. Striking a perfect balance between security and accessibility, we keep your business running smoothly, without having to worry about a data breach catching you unawares.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help your organization implement and improve the proper authentication, integrity, confidentiality, availability, and nonrepudiation of its sensitive information.

